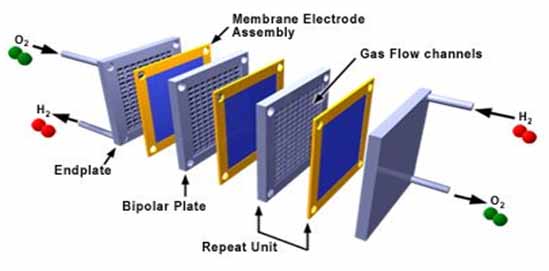
Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells (PEMFC) and MEA
Proton exchange membrane fuel cells, also known as polymer electrolyte membrane (PEM) fuel cells (PEMFC), were specifically developed for lower temperature and pressure application (50 to 100?C). The slate of applications include transportation, stationary, and portable devices. The key characteristic of PEM is a special polymer electrolyte membrane.
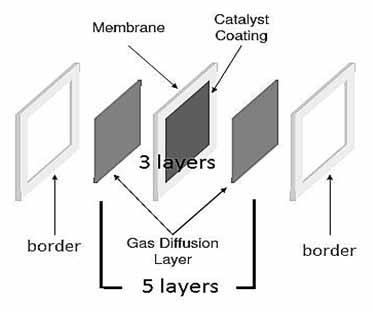
The Membrane Electrode Assembly (MEA)
Within the membrane electrode assembly (MEA), the PEM is sandwiched between two electrodes that are coated by catalysts. The electrodes are insulated from each other by the membrane. These two electrodes make up the anode and cathode respectively. The PEM is proton permeable but electrically insulating. This barrier allows for the transport of the protons from the anode to the cathode through the membrane but forces the electrons to travel around a conductive path to the cathode.
Performance
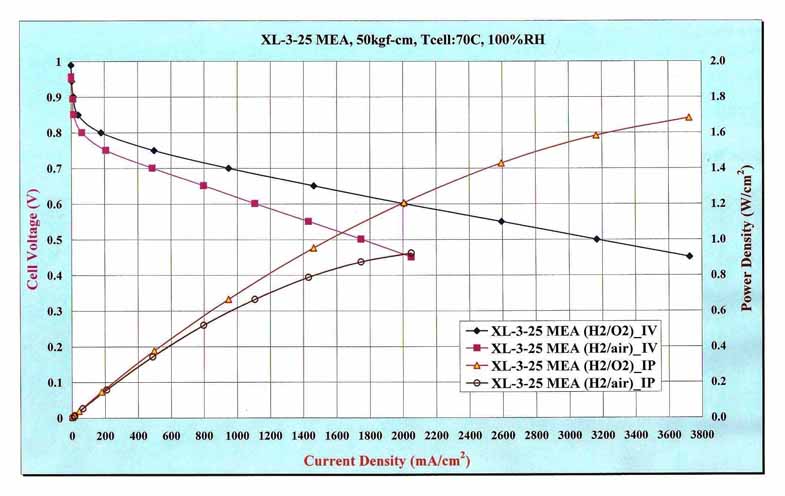
The performance of the MEA depends largely on the oxygen supply, operating conditions, and the quality of the single cell or stack assembly. Typical performance curves of our MEAs, taken under a non-pressurized condition for either cathode or anode, are shown below. These measurements were collected and validated by a third-party institution, the renowned Industrial Technology Research Institute (ITRI) of Taiwan.
Other Information
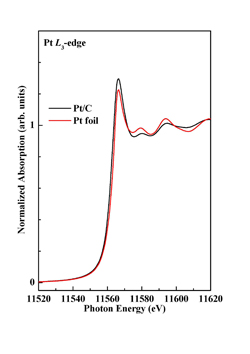
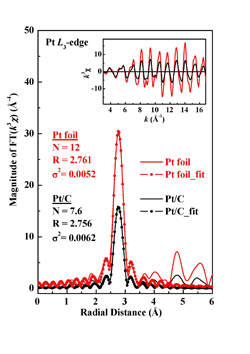
Electro-catalysts used in YZ catalyst coated membranes (CCM): The catalysts in our YZ catalyst coated membranes (YZ CCM) are purchased from well-known Japanese and U.K. suppliers. We measured the quality of our catalysts at the National Synchrotron Radiation Research Center BL17C1 in transmission mode.